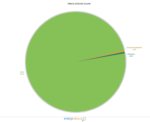
As reported by the National Energy Board (NEB) in 2017, two-thirds of the electricity sources in Canada come from renewable energy, with a combination of wind power, hydroelectric generation, solar power and even biomass energy. Despite a reputation for a fossil-fuel-based economy, over 80% of our electricity is produced via net-zero carbon sources with hydroelectricity accounting for 60% of our total production, per the Canada Energy Regulator.
Yet, there is a lot more to know about energy distribution in Canada. In order to understand the Canadian energy market, you need to go way beyond voltages, rates and your utility bills. Generating electricity in such a large country requires an understanding of the particularities of each province and its power frameworks.
Read on to learn not only how much of Canada’s energy is renewable, but what are the main sources (clean or not) of electricity generation by province.

What is the cheapest energy source?
Unfortunately, this question doesn’t have a simple answer. There is no particular source of energy that can be evaluated on those grounds.
Different provinces rely on different resources available locally to power their grid, meaning that even if one source was cheaper overall, it may be the most expensive option to consider depending on your province. For example, despite Canada largely relying on hydroelectricity, a few prairie provinces and northern territories rely primarily on fossil fuels due to availability. So, it may be more expensive or even impossible to use hydroelectricity in those areas.
It doesn’t get any easier if you compare a singular unit of energy as a commodity either. How utilities are calculated varies between provinces, with places like Ontario charging different rates depending on the time of use; or Alberta and Ontario having deregulated markets which allow you to get different rates depending on your provider and plan while others have regulated markets in which prices are set.
According to NRCan, British Columbia, Manitoba and Quebec have the lowest electricity prices. This comes as no surprise considering that these three provinces have access to an abundance of hydroelectricity projects that are able to meet greater demand at a low cost.
Where does electricity come from? The main electricity sources in Canada
Electricity is everywhere in our lives. It’s quite difficult to imagine how things would be nowadays if there weren’t any electrical wires connecting almost everything everywhere. Still, we don’t know much about it. It is so natural to just plug devices here and there that we don’t even think about how the magic happens.
The electricity industry is responsible for generation, transmission and distribution. Electricity can be generated from many sources, be it solar or hydroelectricity. All of them, however, are based on the same concept: creating energetical movements until an electrical current is generated.
If you didn’t miss your Physics 101 classes, you know that energy can’t be created or destroyed. To generate electricity, energy generators use turbines or motors to transform other types of energy — such as mechanical, nuclear or chemical — into electricity.
In Canada, one of the main energy sources is hydroelectricity, which accounts for 59 percent of the generation grid, according to a 2016 report by Natural Resources Canada (NRCan).
Hydroelectricity is considered green energy by many experts and contributes greatly to Canada’s top-10 ranking among the world’s largest producers of electricity. The country currently ranks as the sixth-largest electricity generator in the world, and the second-largest electricity exporter globally. Nearly 11 percent of the electricity generated in Canada is exported to the United States.
Fossil fuels and coal power are still significant electricity sources in Canada, but their use varies substantially from province to province. While Ontario uses only 0.1 percent of petroleum to generate electricity, Nunavut’s electricity is 100 percent oil-based.
Which province is Canada’s largest producer of hydroelectricity?
When you take a look at the electricity generation province per province, you notice the importance of hydroelectricity in many Canadian regions. According to NRCan, five provinces use hydroelectricity to produce 80% or more of their electricity. While Quebec is the largest generator of hydroelectricity, generating with it over 200 TWh of electricity, Manitoba uses hydro to generate the greatest percentage of its energy at 97%. Alberta only gets 3% of its electricity from hydro.
- Manitoba: 97.0%
- Newfoundland and Labrador: 96%
- Quebec: 94%
- British Columbia: 87%
- Yukon: 80%
- Northwest Territories: 47%
- Ontario: 24%
- New Brunswick: 22%
- Saskatchewan: 15%
- Nova Scotia: 10%
- Alberta: 3%

The main electricity sources by province in Canada
If you’re interested to know what are the main electricity sources in your province, read on to know about power generation in Canada according to each region.
NOTE: The sum of components may not equal 100% because of rounding by the official agencies, such as the National Energy Board and Natural Resources Canada.
Alberta
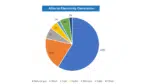
Electricity sources in Alberta are unique because of the province’s abundance of oil, gas and coal. Together, coal and natural gas are responsible for 89 percent of the energy generation in the Alberta electricity market. As an illustration, electricity in cities such as Edmonton and Calgary is mainly generated by natural gas. However, Alberta is continuing to diversify its electricity portfolio and its electricity market is rapidly developing.
- Natural gas: 60%
- Coal and coke: 7%
- Wind: 20%
- Solar: 6%
- Hydro: 5%
- Biomass or geothermal: 2.0%
- Petroleum: 0.1%
- Other: 2.0%
Ontario
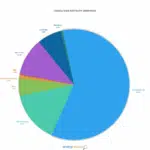
According to 2022 data from the Ontario Energy Board (OEB), the main electricity sources in Ontario are nuclear energy and water power. Ontario generates and relies on the most nuclear power in Canada. However, the province presents a very diverse grid of electricity sources. Check the detailed information below.
- Nuclear energy: 51%
- Water power: 25%
- Wind: 9.9%
- Natural gas: 10.2%
- Solar: 2.5%
- Bioenergy: 0.4%
- Other: 0.9%
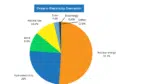
British Columbia
As of 2020, BC produced 5.38 billion cubic feet per day of natural gas, which accounts for 35% of Canadian natural gas production. Despite this, 87% of it of its production is derived from hydroelectricity. Over 95% of electricity generated is clean and renewable. Hence the main electricity provider is named BC Hydro. According to CER, British Columbia generated a total of 64.3 TWh in 2019.
- Hydro: 87.8%
- Natural gas: 4.0%
- Petroleum: 0.5%
- Wind: 2.6%
- Biomass or geothermal: 5.0%
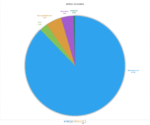
Saskatchewan
In case you were wondering where Saskatchewan gets its electricity, Saskatchewan is the 3rd most reliant on fossil fuels, generating 76% of its electricity from a combination of natural gas and coal. The following are the sources of electricity generation for SaskPower
- Coal and coke: 39%
- Natural gas: 37%
- Hydro: 11%
- Wind: 9%
- Solar less than 0%:
- Biomass and geothermal: 0.5%
- Other: 4%
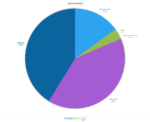
Manitoba
When you ask yourself what is the most common source of electricity in Manitoba, it’s almost impossible not to think of hydro. If that’s not your case, it’s time for you to know that almost all the electricity generated in the province comes from water power. According to Manitoba Hydro, the province is fitted with 16 hydroelectric generating stations, with its oldest built upon the Grand Rapids and the largest on the Nelson River.
- Hydro: 97.0%
- Wind: 3.0%
- Biomass or geothermal: Less than 1.0%
- Coal and coke: Less than 1.0%
- Petroleum: Less than 1.0%
- Natural gas: Less than 1.0%
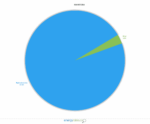
Yukon
Electricity in Yukon also comes mainly from hydro sources. The province presents one of Canada’s largest hydro resources with four hydro plants with a total capacity of 95 megawatts.
- Hydro: 80.0%
- Natural gas: 20.0%
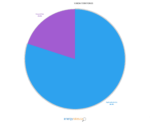
Northwest Territories
In the Northwest Territories, hydro and oil play a major role in generating electricity. Together, these two sources represent about 84 percent of the region’s electricity production.
- Hydro: 47.0%
- Petroleum: 37.0%
- Natural gas: 14.0%
- Wind: 2.0%
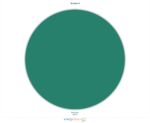
Nunavut
According to NEB data from 2016, the electricity generation grid in Nunavut is remarkable. See for yourself. Qulliq Energy Corporation is the sole provider of electricity in Nunavut. The province is vast with no shared transmission grid to distribute electricity to its 25 isolated communities or local sources from which to generate power. Instead, they rely exclusively on imported petroleum to heat their homes, giving us the unique breakdown seen below.
- Petroleum: 100.0%
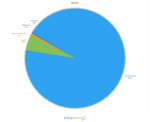
Quebec
In 2015, Quebec used more electricity than any other Canadian province — around 35 percent of the country’s energy use, as reported by NRCan. According to the study, provinces with abundant and cheap electricity from large-scale projects tend to use more electricity per household. In case you don’t know, the majority of such electrical power comes from hydroelectricity. Quebec is the largest generator in Canada, with most of that being hydropower. More than 200 TWh of electricity is produced from hydroelectricity. The province is also home to the Robert-Bourassa hydro plant; the largest in Canada! Below, you can take a deeper look at the Quebec energy sources.
- Hydro: 94.0%
- Wind: 5.0%
- Biomass and geothermal: 0.7%
- Petroleum: 0.2%
- Natural gas: 0.1%
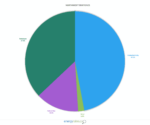
New Brunswick
New Brunswick is tied with Ontario for having the most diverse electricity generation system in Canada. Its power comes from at least seven different sources. Another thing it has in common with Ontario? Getting the most electricity from nuclear energy.
- Nuclear energy: 37.6%
- Hydro, wave and tidal: 21.8%
- Natural gas: 14.9%
- Wind: 6.9%
- Biomass and geothermal: 4.0%
- Coal and coke: 13.9%
- Petroleum: 1.0%
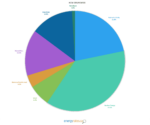
Newfoundland and Labrador
Following in the footsteps of Manitoba and BC, Newfoundland and Labrador’s main electricity source is water power.
- Hydro: 96.0%
- Petroleum: 3.0%
- Natural gas: 0.6%
- Wind: 0.4%
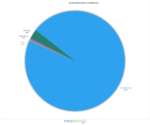
Nova Scotia
The electricity mix in Nova Scotia is almost as unique as New Brunswick’s. There are at least six Nova Scotia electricity sources, with coal as the leading one.
- Coal and coke: 52.0%
- Natural gas: 22.0%
- Wind: 11.0%
- Biomass and geothermal: 3.0%
- Hydro, wave and tidal: 10.0%
- Petroleum: 2.0%
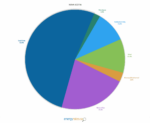
Prince Edward Island
PEI is entirely unique among the Canadian provinces being the leader in wind power generation. In fact, almost all of its electricity comes from wind, making it one of the greenest provinces alongside British Columbia. The catch is, however, most electricity consumed is imported from New Brunswick. Since 2005, the province’s wind capacity increased by over 1200%.
- Wind: 99.0%
- Petroleum: 0.5%
- Biomass or geothermal: 0.5%